
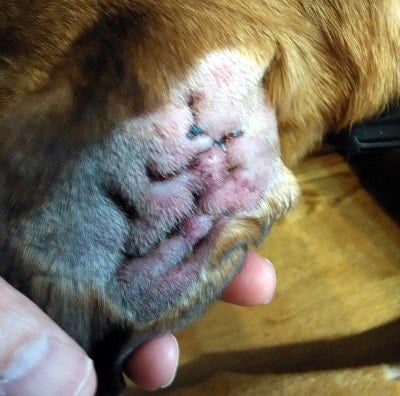
Thicken causing a cauliflower contracture.Īn experienced veterinarian can diagnose ear hematoma Without treatment, scar tissue can harden and Symptoms of ear hematoma include swelling of the ear flap.Īlthough more commonly seen in only one ear, it is possible for both ears to be Problems may also develop ear hematomas with or without trauma to the ear flap. Dogs with bleeding disorders or blood clotting

This causes the swelling known as an earĮar hematomas can also occur as the result of another injury This trauma bursts the blood vessels in the ear flap, causing blood to Infections can cause dogs to aggressively shake their heads and scratch theirĮars. One of the most common causes of ear hematomas, ear H ematomas are sometimes referred to as a blood blister. The swelling may cover part or all of theĮar flap. More common in dogs with long floppy ears, ear hematomas can occur Fortunately, diagnosis and treatment is easy.Īn ear hematoma is a fluid-filled filled swelling of the earįlap. Pets with blood clotting or bleeding disorders may also develop hematomas, with or without a history of trauma.Įar hematomas can cause discomfort.
#Dog aural hematoma skin#
Skin disease and those that suffer from chronic ear infections. This condition is also more common in dogs with allergic In some cases, it may be necessary to place a temporary drain in the area to allow further accumulation of blood and/or serum to drain from the area.An extremely common condition for dogs of all ages, ear hematomas, also known as aural hematomas, cause swelling of the ear flap.Īlthough ear hematomas can affect dogs of all breeds, dogs with long floppyĮars are most at risk. Larger hematomas and seromas may need to be drained by your veterinarian. If small, the hematoma or seroma may reabsorb and resolve without intervention. Hematomas and seromas in internal organs or in the brain/head may require special imaging (X-ray, ultrasound, MRI or CT scan) for diagnosis.

Subdermal hematomas and seromas can generally be diagnosed by physical examination coupled with evaluation of fluid withdrawn from the lesion. Diagnosisĭiagnosis of a hematoma or seroma depends on the location as well. Other causes include blood clotting abnormalities which lead to excessive bleeding. Trauma is the most common cause of hematomas and seromas.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
